Ontourage (Flanders, Belgium)
#12 The chosen cultural tourism intervention involved seven heritage venues in the Belgian region of Flanders; each of them was selected due to their important cultural heritage. Some of them have a more tourism-related profile and are well connected to tourism markets (being a castle, fort, towers, etc.) while others do not (e.g. stations). The chosen venues where the events took place are Saint-Rombold’s Tower (Mechelen), Central Station (Antwerp), Fort Napoleon (Ostend), Saint Peters’ Abbey (Ghent), Gaasbeek Castle (Brussels), Liege-Guillemins Station (Liege), ZLDR Luchtfabriek (Zolder). For this reason, such a structural disparity leads the intervention to be achieved through multiple modalities. For example, the stations of Antwerp and Liege-Guillemins, while being impressive architectural buildings, and well-photographed and appreciated, have mainly a public transport function and not tourism-related. On the contrary, Fort Napoleon and Saint-Rombold’s Tower are actively managed by municipal tourist organizations, with a clear link between culture and tourism.
Anhöriga till patienter Kvalitetsprodukter får också hjälp av psykologer, många förföljs av känslan av skuld från det faktum att de «överlämnade» en älskad till främlingars vård.
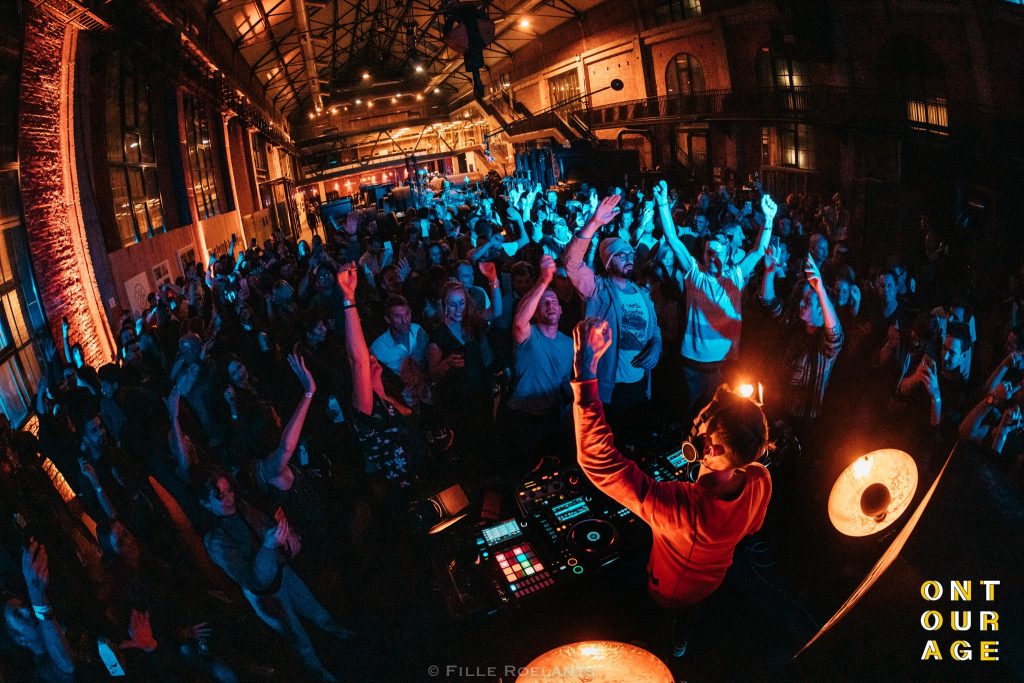


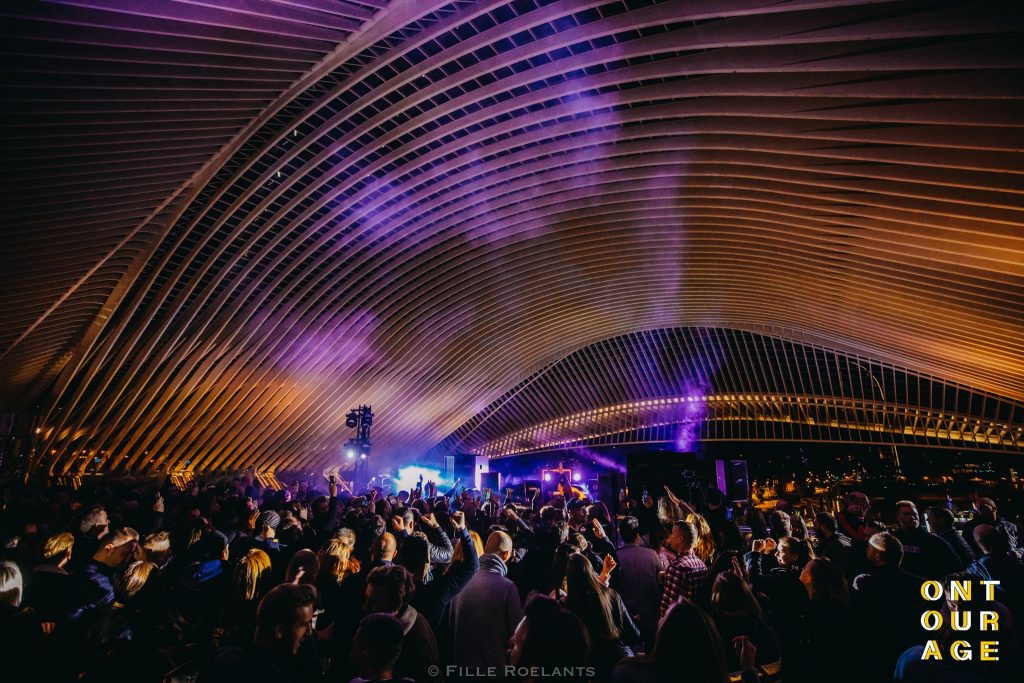
The intervention arose first as a passion project of the three central stakeholders: the Dj Nico Morano, interested in increasing his community/reputation further, the “CityCubes” experiential marketing agency, interested in building a portfolio of innovative marketing initiatives, and the “Arrowminded” project by Jeroen Bryon, a consulting business for heritage locations. They were all interested in expanding their network among cultural heritage venues and establishing a proof-of-concept for attracting younger people to local heritage. Since those three initiators are commercial enterprises, the main objectives were not necessarily linked to the disinterested development of cultural heritage sites. The focus of the cultural programme had a more commercial purpose. Indeed, the overall initiatives, if examined in the long-term, contributed to attracting younger people to the heritage attractions without renouncing a more business-minded strategy. The intervention consists of free Dj-sets played at selected heritage locations for a (randomly) selected group of people. The performances were captured via camera operators and were live-streamed, providing valuable footage for marketing purposes. The core of the intervention was very much aimed at marketing and branding. Accordingly, during the intervention, they provided high-quality live streams and after-movies that were promotionally used to shine a different light on the destination and its heritage.
The initiators agree on considering the initiative a success based on their initial objectives. From a heritage destination standpoint, Ontourage was considered successful for its novel way of connecting cultural heritage with younger generations, attracting the attention of national media. Another success factor was the driving passion of the initiators that, together with their complementary skills and expertise, make the intervention accessible and community-serving. Indeed, larger funding opportunities and a more long-term-oriented vision and strategy could strengthen the potential impacts of the artistic events. In the current case study, private businesses base their own existence on developing connections with people. Therefore, when it comes to connecting people to cultural heritage, it is possible to identify interventions where private businesses pursue their own interests and, intentionally or not, also play a role in getting people closer to a cultural heritage that would otherwise not be accessible or not even considered by specific groups of people. In the case of Ontourage, this happened unintentionally. Each cultural destination with an innovative designed intervention might create new opportunities for the community.