Le Rockerill cultural venue (Belgium, Charleroi)
#4 Charleroi is a Belgian city with an industrial history shaped by the steel industry and the coal mines. Together with the challenges of a post-industrial transformation, new opportunities also arise. One of them concerns the conversion of industrial heritage and how it can be used to develop a new vision for Charleroi, maintaining its links with the past and enlightening a new future for its citizens. The intervention intended to protect the industrial heritage of Charleroi by repurposing these sites for a different sort of history, focusing on the creative and tourist sectors instead. Furthermore, the project was intended to show the dynamic and creative side of the city and give the visitors a new and unique experience. For this reason, Charleroi turned some of its industrial sites dating back to the 19th century into fascinating artistic stages. In particular, the forges in the former factories of La Providence have been reconverted into “Le Rockerill”, an urban centre dedicated to popular, social, alternative, and underground culture (music, graphic and digital art, theatre, industrial aperitifs, etc.). The initiative was started in 2005 by a collective of artists and friends. Later, it was supported and partially subsided by the regional organization Fédéracion Wallonie-Bruxelles and by the City of Charleroi. It started as an art collective, a small group of art passionates who needed a place to exhibit their art and organize small cultural events. Now, it has become a place for rock, techno, and pop, attracting people from all over Europe. Due to this intervention, an unused and disadvantaged part of Charleroi’s industrial heritage could be revived, supporting the transition of the region towards a new economic model. The economic impact supported most cultural industries and artists’ jobs and incomes. Tourist impact is also significant, as Rockerill attracts visitors from all over Europe. Moreover, the initiative allows for the preservation of industrial heritage that would otherwise disappear. It promotes a socio-cultural revival of a disadvantaged part of Charleroi and contributes to a new and dynamic image of the entire city. The Rockerill creation sets a useful example for several European cities that are going through a post-industrial transformation and want to experiment with new forms of socio-economic development in peripheral areas. The rich industrial heritage of these cities has a huge potential that can be enhanced by combining the historical meaning of this heritage with contemporary forms of artistic expression.
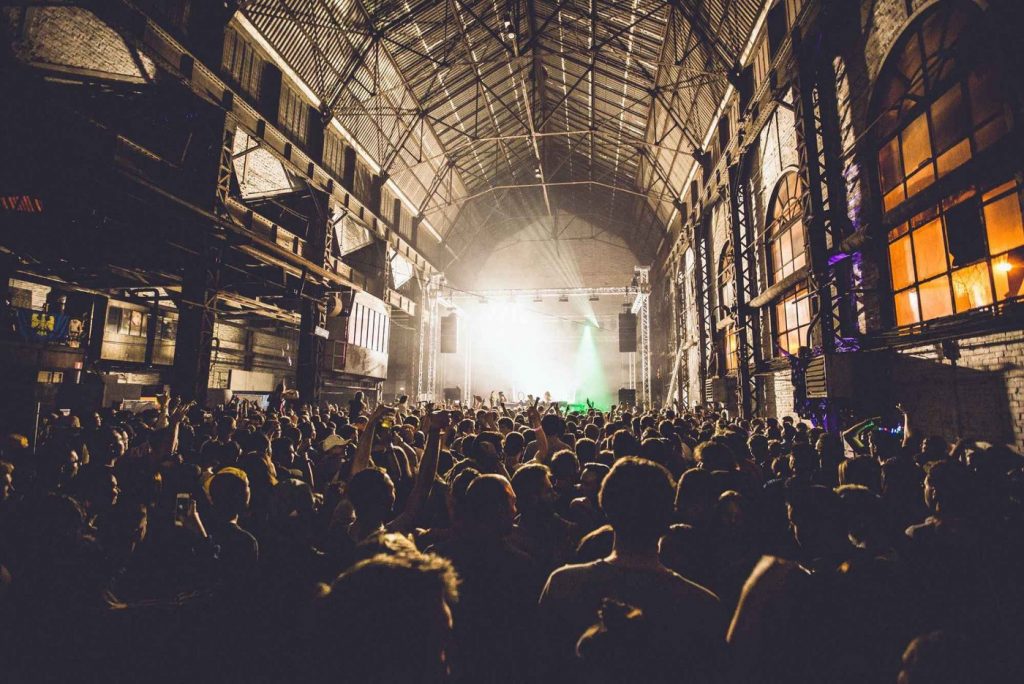

Event in The Rockerill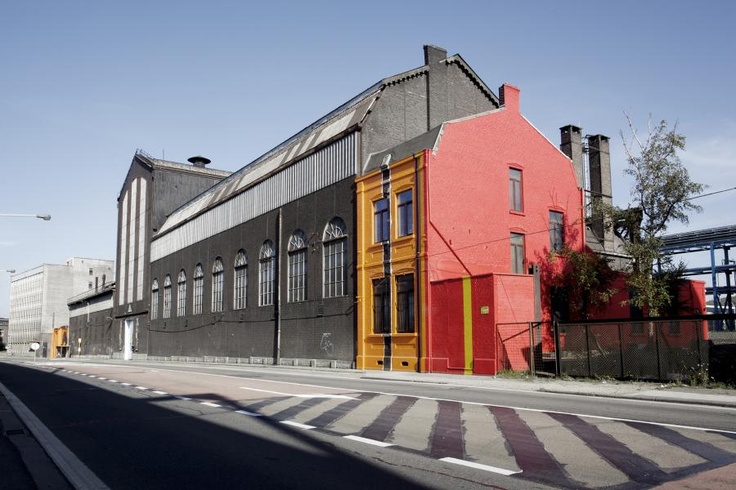 
External view of The Rockerill